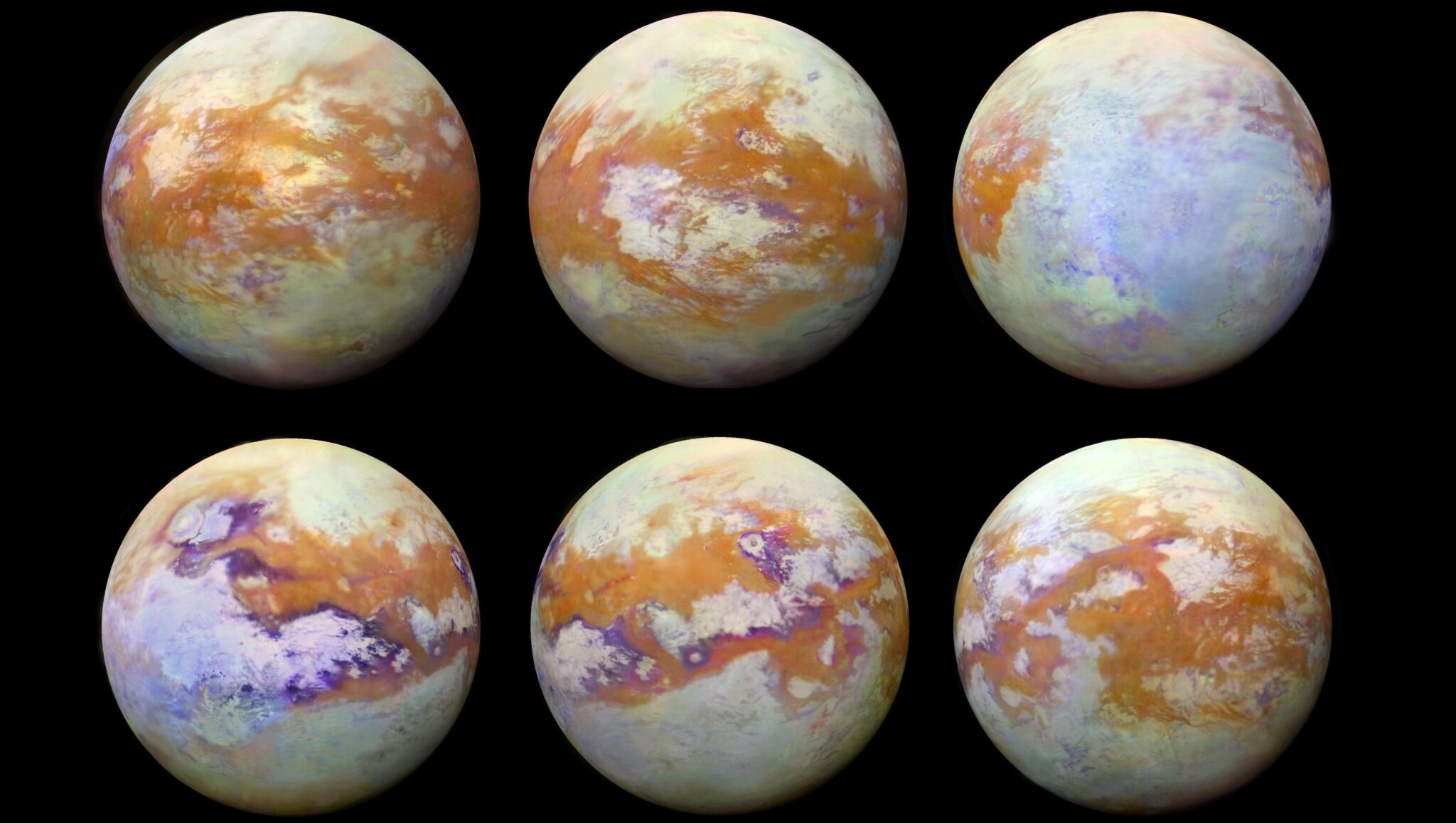
Methane clouds on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, are greater than only a celestial oddity — they’re a window into one of many photo voltaic system’s most advanced climates.
Till now, mapping them has been sluggish and grueling work. Enter AI: a workforce from NASA, UC Berkeley and France’s Observatoire des Sciences de l’Univers simply modified the sport.
Utilizing NVIDIA GPUs, the researchers educated a deep studying mannequin to investigate years of Cassini information in seconds. Their strategy might reshape planetary science, turning what took days into moments.
“We had been in a position to make use of AI to vastly velocity up the work of scientists, growing productiveness and enabling inquiries to be answered that will in any other case be impractical,” stated Zach Yahn, Georgia Tech PhD pupil and lead creator of the research.
Learn the total paper, “Fast Automated Mapping of Clouds on Titan With Occasion Segmentation.”
How It Works
On the mission’s core is Masks R-CNN — a deep studying mannequin that doesn’t simply detect objects. It outlines them pixel by pixel. Skilled on hand-labeled pictures of Titan, it mapped the moon’s elusive clouds: patchy, streaky and barely seen by way of a smoggy ambiance.
The workforce used switch studying, beginning with a mannequin educated on COCO (a dataset of on a regular basis pictures), and fine-tuned it for Titan’s distinctive challenges. This saved time and demonstrated how “planetary scientists, who might not at all times have entry to the huge computing assets essential to coach giant fashions from scratch, can nonetheless use applied sciences like switch studying to use AI to their information and initiatives,” Yahn defined.
The mannequin’s potential goes far past Titan. “Many different Photo voltaic System worlds have cloud formations of curiosity to planetary science researchers, together with Mars and Venus. Comparable know-how may additionally be utilized to volcanic flows on Io, plumes on Enceladus, linea on Europa and craters on strong planets and moons,” he added.
Quick Science, Powered by NVIDIA
NVIDIA GPUs made this velocity attainable, processing high-resolution pictures and producing cloud masks with minimal latency — work that conventional {hardware} would battle to deal with.
NVIDIA GPUs have change into a mainstay for area scientists. They’ve helped analyze Webb Telescope information, mannequin Mars landings and scan for extraterrestrial alerts. Now, they’re serving to researchers decode Titan.
What’s Subsequent
This AI leap is simply the beginning. Missions like NASA’s Europa Clipper and Dragonfly will flood researchers with information. AI can assist deal with it, processing it onboard, mid-mission, and even prioritizing findings in actual time. Challenges stay, like creating {hardware} match for area’s harsh circumstances, however the potential is simple.
Methane clouds on Titan maintain mysteries. Researchers at the moment are unraveling them quicker than ever with assist from new AI instruments accelerated by NVIDIA GPUs.
Learn the total paper, “Fast Automated Mapping of Clouds on Titan With Occasion Segmentation.”
Picture Credit score: NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory

